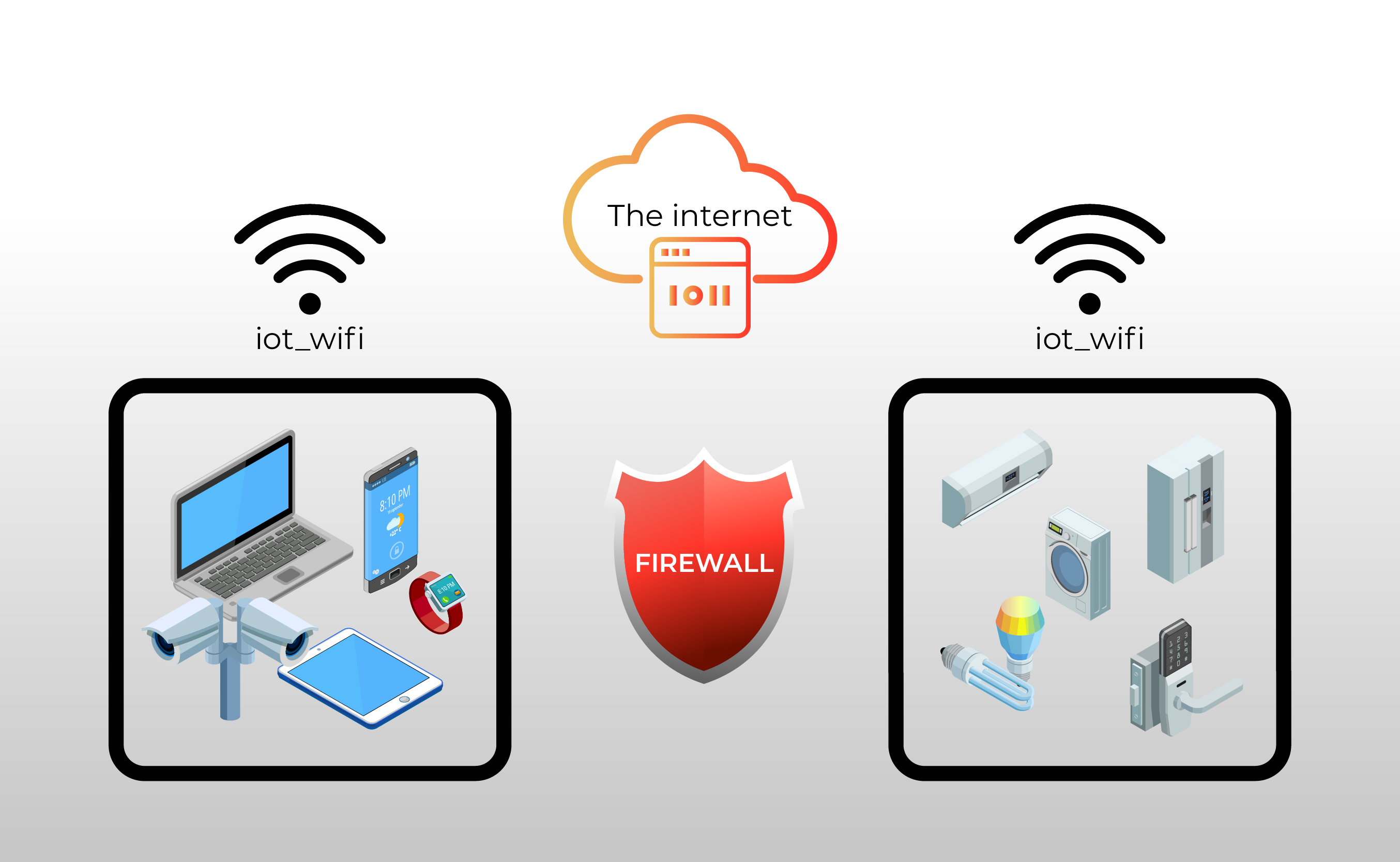
In today's interconnected world, the integration of Internet, Virtual Network Computing (VNC), and the Internet of Things (IoT) has become increasingly vital for businesses and individuals alike. These technologies allow for seamless remote access, device management, and data sharing. However, the presence of firewalls often poses challenges in ensuring secure and uninterrupted communication. Understanding how to navigate these challenges is essential for anyone working with IoT devices or remote desktop systems.
Firewalls are designed to protect networks and devices from unauthorized access, but they can sometimes block legitimate connections, especially when dealing with IoT devices or VNC applications. This creates a need for strategies to bypass or work around these restrictions while maintaining security and compliance. In this article, we will explore how Internet, VNC, and IoT interact behind a firewall, providing practical examples and solutions to common issues.
Whether you're a network administrator, IoT developer, or simply someone interested in remote access technologies, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to overcome firewall-related obstacles. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how to configure and manage VNC and IoT devices securely behind a firewall, ensuring smooth operations and enhanced productivity.
Read also:Pink Hurt Movies A Comprehensive Guide To Heartfelt Stories And Emotional Journeys
Table of Contents
- What is VNC and How Does It Work?
- An Overview of IoT and Its Importance
- Understanding Firewalls: Types and Functions
- How VNC Operates Behind a Firewall
- Challenges of IoT Devices Behind Firewalls
- A Practical Example of VNC and IoT Behind a Firewall
- Security Measures for VNC and IoT Behind Firewalls
- Tools and Technologies to Facilitate VNC and IoT Connectivity
- Best Practices for Managing VNC and IoT Behind Firewalls
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is VNC and How Does It Work?
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop-sharing system that allows users to remotely control another computer. It operates by transmitting keyboard and mouse events from one device to another while displaying the remote desktop screen in real-time. VNC is widely used for remote technical support, accessing files on a home computer from work, or managing servers.
How VNC Works
VNC works by establishing a connection between a client and a server. The server runs on the computer being accessed, while the client is installed on the device used to control the remote desktop. Once connected, the client sends input commands (like mouse clicks or keyboard strokes) to the server, which processes them and sends back the updated screen display.
- Client-Server Model: VNC operates on a client-server architecture, where the server hosts the desktop environment, and the client accesses it.
- Protocols Used: VNC typically uses the Remote Framebuffer (RFB) protocol for communication.
- Platform Independence: VNC is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
An Overview of IoT and Its Importance
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices range from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, and they play a crucial role in automating tasks, improving efficiency, and providing real-time insights.
Key Benefits of IoT
IoT has revolutionized various industries by enabling smarter decision-making and streamlined operations. Some of its key benefits include:
- Automation: IoT devices can automate repetitive tasks, reducing human intervention and errors.
- Data Collection: IoT sensors gather vast amounts of data, which can be analyzed to uncover trends and patterns.
- Remote Monitoring: IoT allows users to monitor and control devices from anywhere, enhancing convenience and flexibility.
Understanding Firewalls: Types and Functions
A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted network and untrusted networks, such as the internet, to prevent unauthorized access.
Types of Firewalls
There are several types of firewalls, each designed to address specific security needs:
Read also:Crypto30xcom Regulation Understanding The Legal Framework And Compliance
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls: These firewalls examine packets of data and allow or block them based on predefined rules.
- Proxy Firewalls: Acting as intermediaries, proxy firewalls filter requests to hide the identity of the originating device.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: These firewalls track the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of the traffic.
How VNC Operates Behind a Firewall
When using VNC behind a firewall, the firewall may block the default ports used for VNC communication, such as port 5900. This can prevent the client from connecting to the server, disrupting remote access. To overcome this, several techniques can be employed.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a common solution that involves configuring the firewall to allow traffic on specific ports used by VNC. By opening the necessary ports, the firewall permits VNC connections while still blocking unauthorized access.
Using SSH Tunnels
Another effective method is to use Secure Shell (SSH) tunnels. SSH tunnels encrypt VNC traffic, ensuring secure communication even when passing through firewalls. This approach not only bypasses firewall restrictions but also enhances security.
Challenges of IoT Devices Behind Firewalls
IoT devices often face unique challenges when operating behind firewalls. These challenges stem from the need for constant connectivity and the potential security risks associated with exposing devices to the internet.
Common Issues
- Port Blocking: Firewalls may block the ports required for IoT communication, leading to connectivity issues.
- Security Vulnerabilities: IoT devices are often targeted by cybercriminals, making it crucial to balance accessibility with security.
- Configuration Complexity: Managing multiple IoT devices behind a firewall can be complex, especially in large-scale deployments.
A Practical Example of VNC and IoT Behind a Firewall
Let's consider a scenario where a network administrator needs to access an IoT device remotely using VNC. The IoT device is located behind a corporate firewall, and the administrator must configure the network to allow secure VNC access.
Step-by-Step Solution
- Identify Required Ports: Determine the ports used by the VNC server and IoT device.
- Configure Firewall Rules: Set up port forwarding or create exceptions in the firewall to allow traffic on these ports.
- Enable SSH Tunneling: Use SSH to encrypt VNC traffic and ensure secure communication.
- Test Connectivity: Verify that the VNC client can successfully connect to the IoT device.
Security Measures for VNC and IoT Behind Firewalls
While enabling VNC and IoT communication behind firewalls is essential, it is equally important to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and devices.
Best Security Practices
- Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that all VNC and IoT devices are protected with strong, unique passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second method.
- Regularly Update Firmware: Keep IoT devices and VNC software up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
Tools and Technologies to Facilitate VNC and IoT Connectivity
Several tools and technologies can simplify the process of managing VNC and IoT devices behind firewalls. These solutions provide features like automated port forwarding, secure tunneling, and centralized device management.
Popular Tools
- Ngrok: A tool that creates secure tunnels to localhost, bypassing firewall restrictions.
- Zerotier: A software-defined networking platform that allows devices to communicate as if they are on the same local network.
- TeamViewer: A remote desktop application that includes built-in firewall traversal capabilities.
Best Practices for Managing VNC and IoT Behind Firewalls
To ensure smooth and secure operations, it is essential to follow best practices when managing VNC and IoT devices behind firewalls. These practices help minimize risks and optimize performance.
Recommended Practices
- Limit Access: Restrict VNC and IoT access to authorized users only.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Regularly analyze network traffic to detect and respond to potential threats.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Separate IoT devices from critical systems to reduce the attack surface.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding how Internet, VNC, and IoT interact behind a firewall is crucial for ensuring secure and efficient remote access. By following the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, you can overcome firewall-related challenges and maximize the potential of these technologies.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Have you encountered any unique challenges while managing VNC or IoT devices behind a firewall? Additionally, feel free to explore our other articles for more insights into networking and cybersecurity.